Project based learning is a very successful learning technique used where the problem is the starting point of learning technique. Students get to work in group seeking multiple sources of information and creating authentic products. Project based learning started with the goal to help PHCET engineering students develop the skills, tools and character they will need as future leaders in the world of engineering practice. The benefits are plenty including improved designing of circuits skill, understanding concepts, people and processes in an organisation. The core idea of PBL is that real-world problems capture students’ interest and provoke serious thinking, as the students acquire and apply new knowledge in a problem-solving context.
Department
Automobile and Mechanical Engineering
Pillai HOC College of Engineering & Technology, Department of Mechanical and Automobile Engineering organised PBL on 19th October, 2018 for third year students and 13th October, 2018 for second year students. Totally 66 teams for third year and 36 teams for second year have demonstrated their projects. The necessary equipment and components were provided by the college freely to the students to complete their projects. Evaluation was done by panel of faculties by standard rubrics.
The problem statement for PBL are as follows
Second Year: Skyscraper
- Design and fabricate a skyscraper capable of sustaining a load
- Materials for the structures are limited to polystyrene foam and pencils
- Tallest structure would be appreciated
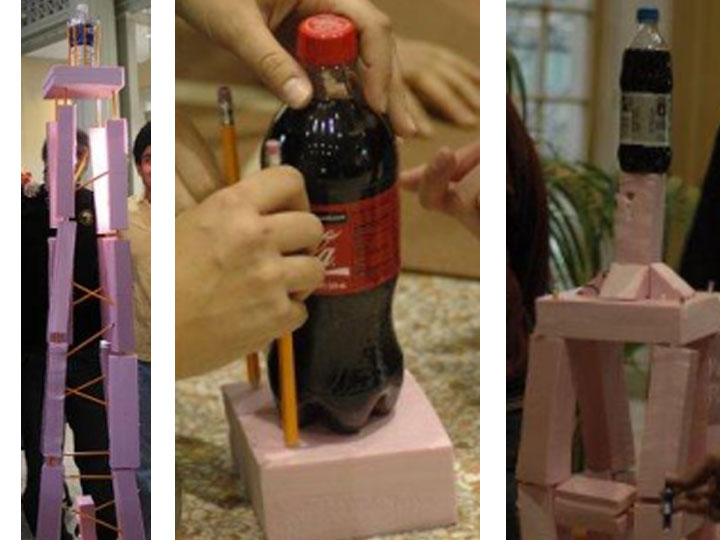


Design a skyscraper capable of:
- Sustaining the weight of a 0.5 litre bottle
- Remaining stable when it is 10º incline
- Minimum height of the structure should be 1 m with minimum 4 links
- Base should not exceed 45cm*45cm area
Technical Objectives
- Document rough ideas / plans for the skyscraper
- Check feasibility of final idea / plan
- Design and document plans for the skyscraper
The evaluation will be done in two stages:
First Evaluation: Explain to the teacher the documents detailing the group’s plans, Design and its Implementation
Final Evaluation: Display the project with a report containing following points:
- Introduction – should include Goals of Project, General Background on skyscrapers, Forces involved, Energy Transformations, Construction methods and Materials used.
- Design (estimation of dimensions of various parts) – Optional
- Computerized (CAD) figures showing assembly and details of the pot
- Cost analysis
- Conclusion
- References (all sources of information should be clearly cited)
- Contribution details of each participant of the group
Related Subjects: Mathematics, Engineering Mechanics, Material Technology, Strength of Material, Production Process, Computer Aided Machine Drawing and Machine Shop Practice
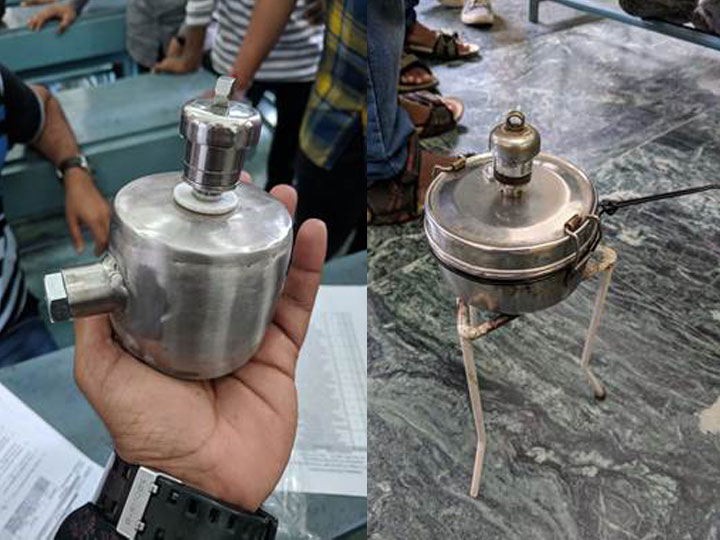
Third Year: Pressure Vessel


Assume Ǭ = 0.47 KJ/s (Heat Supplied by Burner) & mass of water 0.1 Kg to avoid accident use safety valve to relieve excess pressure from the pot.
Note: Pots without safety valve will not be taken for examination.
Learning Activities and Tasks :
- Student should calculate, analyse and make their design.
- Student should calculate the time required to lift the dead weight. The time should not exceed 3 minutes.
- Student must be careful while selecting material and its thickness.
- Student should study the various production process required to build the pot.
The evaluation will be done in two stages:
First Evaluation: Explain to the teacher the documents detailing the group’s plans, Design and its Implementation.
Final Evaluation: Display the project with a report containing following points
- Introduction – should include Goals of Project, General Background on skyscrapers, Forces involved, Energy Transformations, Construction methods and Materials used
- Design (estimation of dimensions of various parts) – Optional
- Computerized (CAD) figures showing assembly and details of the pot
- Cost analysis
- Conclusion
- References (all sources of information should be clearly cited)
- Contribution details of each participant of the group
Related Subjects: Mathematics, Material Technology, Fluid Mechanics, Production Process, Thermodynamics, Heat Transfer, Computer Aided Machine Drawing, Mechanical Measurements and Machine Shop Practice